Visualization
Envision
SMARTS includes a front-end visualization tool called Envision that provides real-time view of the environment state. Envision is built on web-technologies (including React, WebGL, and websockets) allowing it to run easily in the browser. It is composed of a few parts: a client which SMARTS uses directly; a server used for state broadcasting; and the web application where all the visualization and rendering happens.
Run
An example is shown below to run SMARTS with Envision.
$ cd <path>/SMARTS
# Install the dependencies for Envision
$ pip install smarts[envision]
# Build scenarios/sumo/loop
$ scl scenario build --clean scenarios/sumo/loop
# Run the chase_via_points.py example with the loop scenario
$ scl run --envision examples/e2_single_agent.py scenarios/sumo/loop
--envision flag is added to scl run to enable the Envision server. Visit http://localhost:8081/ in your browser to see the environment visualization. Select the simulator instance in the top left drop-down. If you are using SMARTS on a remote machine you will need to forward port 8081.
Data Recording and Replay
For recording, simply feed envision_record_data_replay_path with desired recording output path in gym.make(...).
env = gym.make(
"smarts.env:hiway-v1",
scenarios=args.scenarios,
agents={AGENT_ID: agent},
headless=args.headless,
envision_record_data_replay_path="./data_replay",
)
Currently Envision server needs to be up for data recording to work. Hence, run SMARTS with Envision, such as scl run --envision <examples/example.py> <scenarios/scenario>.
For replay, ensure Envision server is running, then use the following tool - passing in the replay files.
# Here, the recorded file directory is ./data_replay/1590892375a
$ scl scenario replay -d ./data_replay/1590892375a -t 0.1
INFO:root:Replaying 1 record(s) at path=data_replay/1590892375a with timestep=0.1s
Development
Note
This section is only for those interested in editing or developing Envision.
To contribute to Envision it is easiest to start and control the processes manually. Start the Envision server by running
$ cd <path>/SMARTS
# Runs on port 8081 by default
$ python3 envision/server.py --debug
Then start the Envision web application. This requires npm (version >= 6) and node (version >= 12).
$ cd envision/web
# Install dependencies
$ npm install
# Build, run dev server, and watch code changes
$ npm run watch
This development flow currently requires reloading the webpage after any updates.
Save an updated distribution if any changes were made to the Envision web application.
$ cd envision/web
# Saves to envision/web/dist
$ npm run build
Visdom
Use the visdom integration to easily see the image-based observation outputs in real-time. Start the visdom server before running the scenario and open the server URL in your browser http://localhost:8097.
# Install visdom
$ pip install smarts[visdom]
Enable visdom in the SMARTS environment by setting SMARTS_VISDOM_ENABLED. For example:
; ./smarts_engine.ini | ~/.smarts/engine.ini | /etc/smarts/engine.ini | $PYTHON_PATH/smarts/engine.ini
[core]
...
[visdom]
enabled=True
hostname="http://localhost"
port=8097
Start the visdom server:
# 8097 is the default visdom port.
$ visdom -port 8097
Below is a sample visualization of an agent’s camera sensor observations.
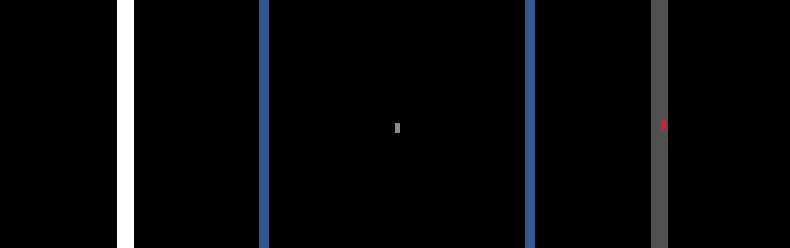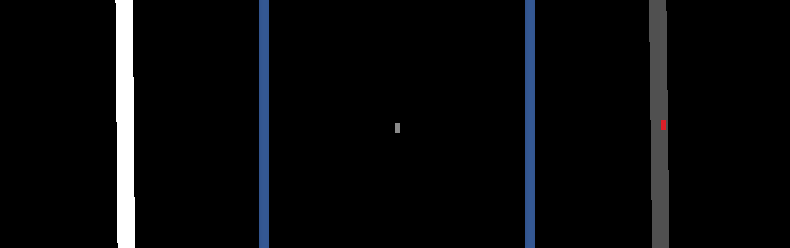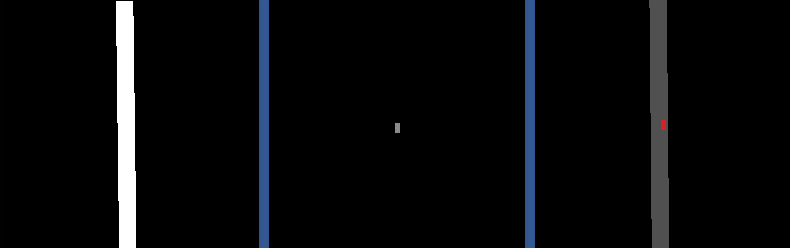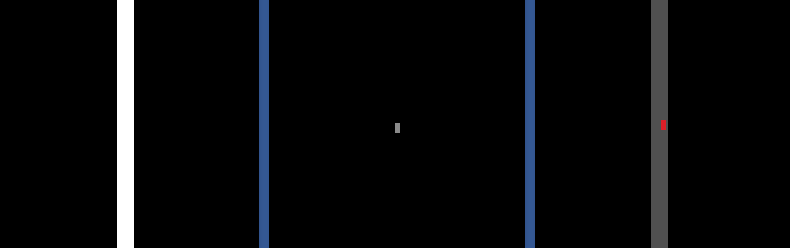
(Left) Drivable area grid map. (Center) Occupancy grid map. (Right) Top-down RGB image.